Data has become a driving force behind successful business decisions and strategies in today’s digital age. When it comes to B2B (business-to-business) interactions, the value of accurate and reliable data cannot be overstated. It serves as the backbone for effective marketing campaigns, sales initiatives, and overall business growth. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the world of B2B data, exploring its significance, sources, types, and the pivotal role it plays in modern-day businesses. Whether you are a marketing professional, sales executive, or a curious entrepreneur looking to leverage data-driven insights, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the complex landscape of B2B data.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.What is B2B data?
B2B data refers to the collection, analysis, and utilization of data related to businesses in the context of business-to-business (B2B) interactions. It includes various types of information that can provide insights into the characteristics, behavior, and needs of businesses, enabling targeted marketing, sales, and strategic decision-making.
Why is B2B data Important?
B2B data forms the foundation of informed decision-making, targeted marketing strategies, and overall business success in the B2B landscape. By leveraging reliable and accurate data, businesses can identify and understand their target audience, uncover market trends, and personalize customer experiences.
B2B data enables organizations to segment their customer base, customize their messaging, and optimize their marketing efforts to reach the right prospects with the right message at the right time. Additionally, B2B data provides valuable insights into the characteristics, behavior, and needs of businesses, allowing for more effective lead generation, sales forecasting, and customer relationship management.
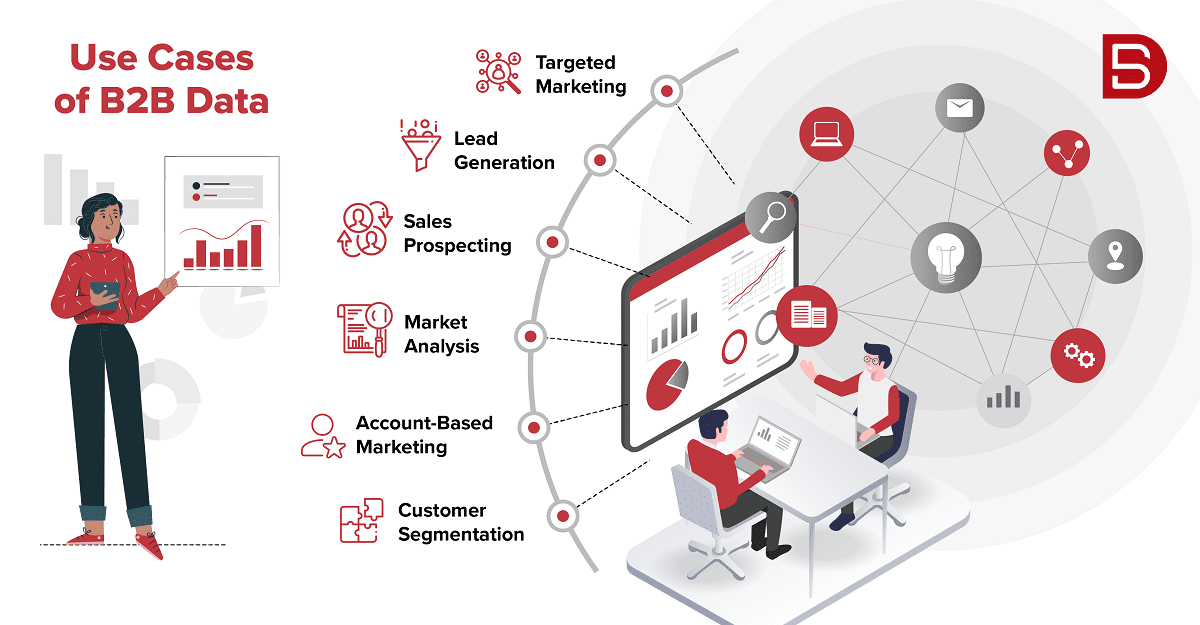
What kind of B2B data is important for you?
The first step is understanding your ICP (Ideal Customer Profile), which will serve as the foundation for your sales cycle. If you target the wrong ICP, you may not make any sales, even if you have a revolutionary product or service.
How does one develop their own ICP? First, choose the kind of businesses that would profit from using your product or service. Second, the buyer personas you want to interact in those organizations, keeping in mind that they should be the decision-maker or a person of significant influence (Not necessarily just the end-user). The following are the fundamental criteria to think about:
Company data
- Which industry or industries are you aiming for? (e.g., Manufacturing, Healthcare, Technology)
- How big should the business be? (For example, 11–50, 200–500, or 1,000+)
- Where is the business situated? (e.g., North America, London, etc.)
Prospect data
- Job title: Which job title/s your prospect should have (e.g., CEO, Head of Sales, Director)
- Job Function: Which department/s should they be employed in? (e.g., Accounting, General Management, Marketing)
- Tenure: How long or little should they have held the position for? (Examples: >3 months, 1 year or more, 10 years or more)
These specifics, or data points, are associated with a contact or account. Once your ICP has been created, you will need the following information before contacting them:
Contact data
- Full name
- Phone number
- Email address
- Social media
The data can be further filtered by adding additional criteria like their previous interactions with your business (via social media, website visits, eBook downloads, etc.), recent company news (like a funding round), technologies they use (whether they use a competitor’s product), or custom tags. These data points all describe various B2B data types that can be used to help you develop the best sales and marketing plan for your company.
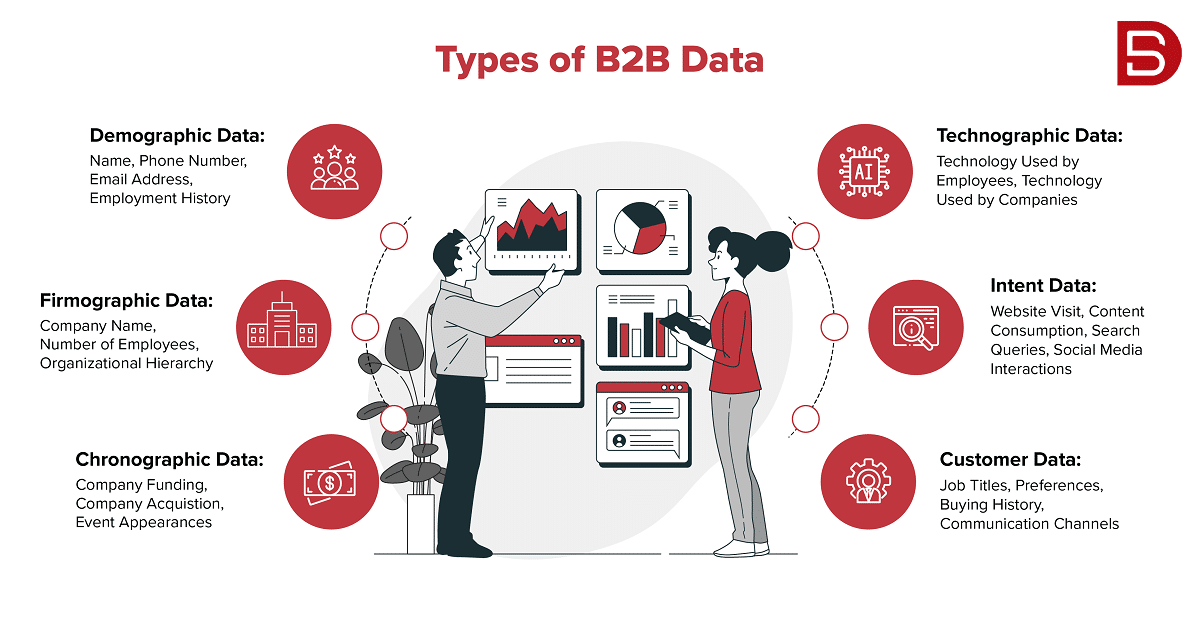
What are the types of B2B data?
The sales and marketing teams can use various B2B data types. These various data types can be used to efficiently target and interact with your potential customers, depending on your product or service and your sales process. Here are some of them:
1. Demographic Data
Demographic data can encompass various personal and geographical factors such as name, physical address, telephone number, location, employment history, and more. These data points help businesses understand the composition of their target market, identify potential customers, and tailor their marketing and sales strategies accordingly.
2. Firmographic Data
Firmographic data provides information about the structure and characteristics of businesses. It includes details such as company size, industry, location, revenue, employee count, ownership type, and organizational hierarchy. Firmographic data helps in segmenting the market, identifying target industries, and tailoring marketing and sales strategies accordingly.
3. Chronographic Data
Chronographic data considers the passage of time about events or any changes that may offer opportunities for sales or marketing. These instances might involve a newly appointed head, recently obtained funding, or hiring new personnel.
This kind of information might be time-sensitive and creates an opening for making an offer right when they need it.
4. Technographic Data
Technographic data focuses on the technology and tools used by businesses. It includes information about software, hardware, IT infrastructure, online platforms, and digital capabilities. Technographic data enables businesses to understand the technological landscape of their target audience, identify opportunities for integration or compatibility, and personalize marketing efforts based on technology preferences.
5. Intent Data
Intent data reveals the online behavior and activities of businesses that indicate their interest or intent to purchase a product or service. It can include website visits, content consumption, search queries, social media interactions, and engagement with marketing campaigns. B2B Intent data allows businesses to identify potential leads, prioritize sales efforts, and deliver targeted messaging to businesses that are actively exploring relevant solutions.
6. Customer Data
While often associated with B2C, customer data is also relevant in the B2B context. It includes information about the individuals within businesses who make purchasing decisions or influence the decision-making process.
Customer data can encompass job titles, roles, responsibilities, preferences, buying history, and communication preferences. This data assists businesses in building relationships, personalizing communications, and delivering targeted messages to key decision-makers.
These are just a few examples of the many types of B2B data available. Businesses can leverage these various types of data to gain a comprehensive understanding of their target audience, optimize marketing and sales strategies, and drive effective business decisions in the B2B marketplace.
What are the sources of B2B data?
After going through the various types of B2B data, you may wonder where you can get it all. As you will see, some of this information is simple to find, while others are more difficult to locate. However, the sources listed below can assist you in finding the information you require:
Social Media
Your prospects will likely be active on social media sites like LinkedIn, Twitter, or YouTube. Although Twitter and YouTube have their uses, LinkedIn is a trendy platform where users include information about themselves to create their profiles.
This information alone can be enough to contact them via the platform. To further tailor your message to them, you can learn more about their interests if they actively post content and interact with other users.
You can create a list of contacts that would fit your ICP using search functions and filters.
Websites
An excellent source of B2B data could be your website. It can draw visitors interested in the trending topics which are published via blogs, guides, and whitepapers. Your website can track various metrics, including traffic volume, traffic source, website conversions, etc. Both website tracking tools and gated content, where users must enter their contact information to download the content, can be used to keep track of each visitor.
Additionally, business websites in your target market can be an excellent source of B2B data. Most have the most recent news releases and a history of their journey thus far. Some websites also have a “Meet the Team” section where people can give a short bio, including their name, job title, and possibly contact information.
Additionally, online platforms can provide more information about businesses, such as funding and investment data about private and public businesses (such as Crunchbase) and employee and customer reviews (e.g., G2 or Glassdoor).
Database Providers
If you want to save time and get right to the point, you can buy the data you need from various sources. You can buy data from a pre-existing database, hire a freelancer to scrape data from the web or use an on-demand data generator.
Their costs and levels of quality primarily distinguish these. Which source is best for you will depend on how you intend to generate leads.
What is B2B Data Sharing?
B2B data sharing refers to the practice of sharing business-to-business (B2B) data between organizations. It involves the exchange of information, insights, and analytics related to businesses and their operations. B2B data sharing can occur through various channels, such as partnerships, collaborations, data marketplaces, and data exchanges.
What are the key aspects of B2B data sharing?
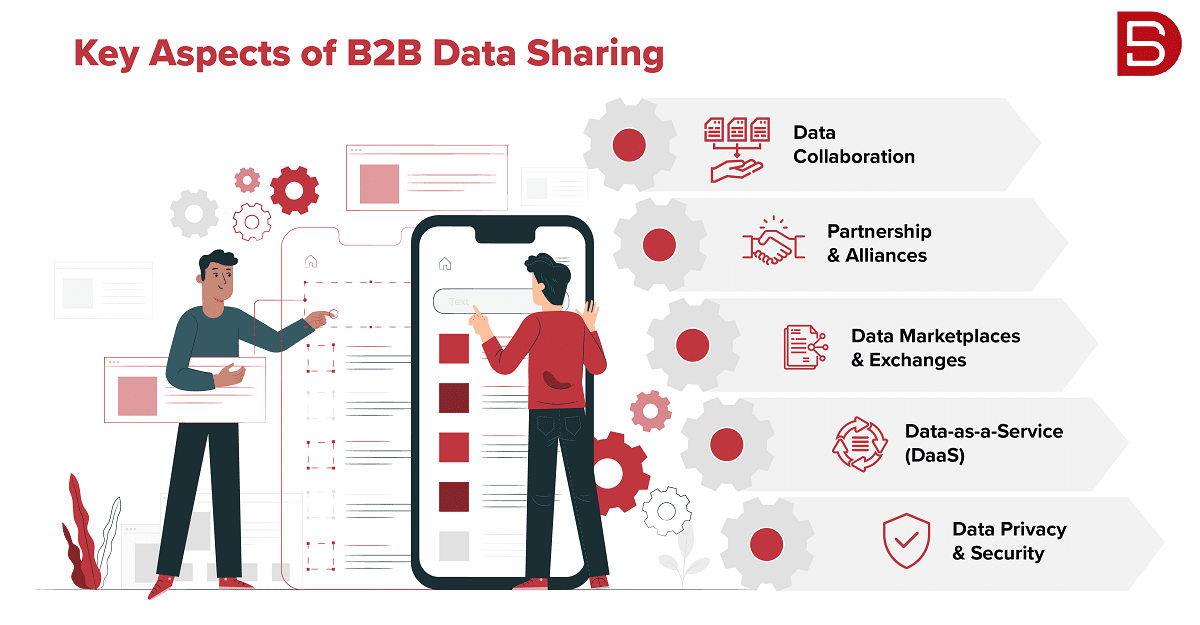
1. Data Collaboration
Businesses may collaborate with each other to share specific datasets or combine their data resources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market, customer behavior, or industry trends. This collaborative approach allows organizations to pool their data assets and derive mutually beneficial insights.
2. Partnerships and Alliances
Companies often form strategic partnerships or alliances to share data. These partnerships can involve sharing customer data, sales and marketing data, or other relevant business information to enhance each other’s understanding of the market, improve targeting, or drive joint initiatives.
3. Data Marketplaces and Exchanges
B2B data marketplaces or exchanges provide platforms for organizations to buy, sell, or trade data. These platforms enable businesses to monetize their data assets by offering them to interested parties or acquire data from other sources to enrich their own datasets.
4. Data-as-a-Service (DaaS)
DaaS providers offer businesses access to various datasets through subscription-based models. These providers collect, curate, and maintain extensive B2B data, allowing organizations to access valuable insights without the need for extensive data collection and management efforts.
5. Data Privacy and Security
B2B data sharing must prioritize data privacy and security. Organizations should ensure compliance with applicable data protection regulations and implement robust security measures to safeguard shared data. Consent and data anonymization techniques may be necessary to protect sensitive information.
How to gather B2B data?
Good quality B2B data is essential and the cornerstone of any effective sales process if you want to run a great campaign and have the best chance of closing sales. The best way to obtain this is by partnering with best B2B data provider. By doing this, you will not have to spend as much time gathering the information and worrying about any data points required to convey your message accurately.
Additionally, some vendors focus on finding clients who fit your ICP and can provide you with lower acquisition costs through bulk purchases. As outlined below, there are two primary sources of B2B data.
On-demand B2B data provider
An on-demand B2B data provider will work with you to create your ICP in detail. You can be assured that whatever data you need for your business is what you will get.
After the criteria have been created and approved, the right b2b data provider will generate these contacts as and when you request them. This means there is no reselling of existing data, and the accuracy of the data points is almost in real-time.
Also, you can take advantage of discounted costs due to bulk purchase of credits which can be used in exchange for contacts only when you need them as this reduces data decay (the rate data degrades over time).
To ensure you only pay for the data you need, you can approve or reject contacts by viewing custom data points, such as job title or department, before the data is purchased. The rejected contacts will be eliminated, and you’ll receive the approved contacts.
B2B database
You can filter a sizable list of contacts from a B2B database vendor using your criteria and buy the required contacts.
A good B2B database provider will update its data as frequently as possible. Many contacts are already generated for you to immediately procure and market to, regardless of your target market and the campaign implemented.
You can buy the data you require when you require it, much like on-demand generation, which helps you prevent data decay while enjoying the benefits of bulk purchases.
What is B2B data used for?
You want to turn contacts into leads and then leads into sales (also known as sales funnel). Your B2B data may come from many places, but it is most likely from one or a combination of inbound, outbound, and paid sources. They can be grouped into one of the following categories depending on the source:
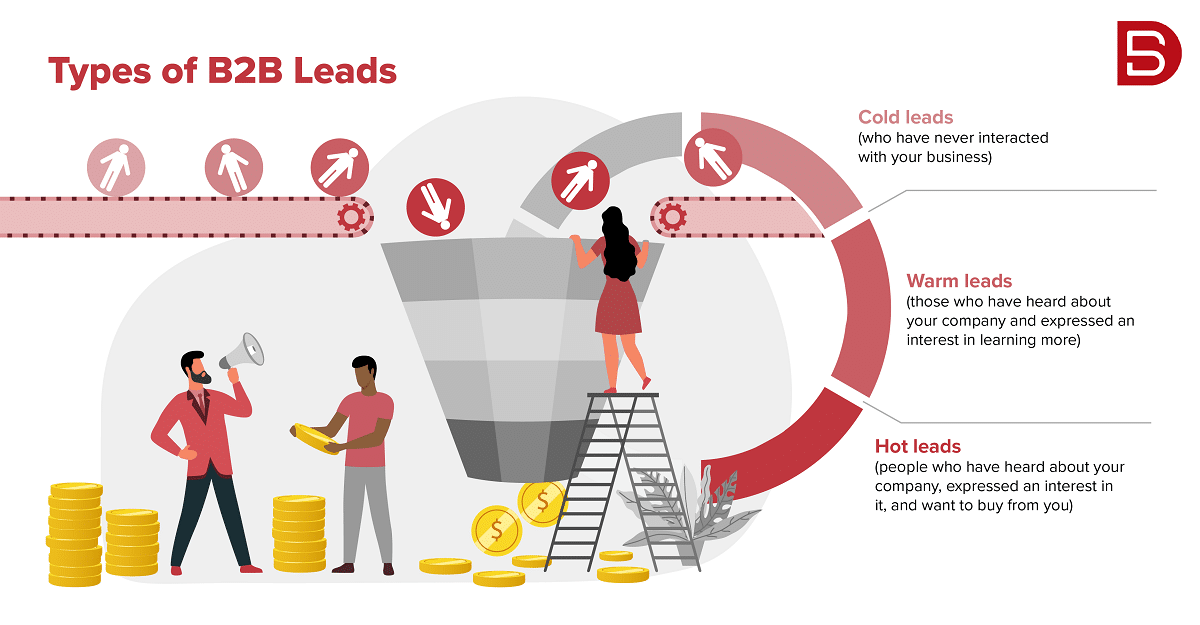
The following examples demonstrate how you can use data to raise awareness of your company and ultimately convert those people into customers.
Demand Generation
Demand generation is a data-driven marketing strategy to increase awareness and interest in what you are offering, whether you want your business to be more well-known or are trying to stand out in a crowded market.
This is accomplished by using your B2B data to offer insightful information. The objective is more about developing trust, authority, and brand positioning in the industry you are operating in rather than driving sales. It is essential to know who your target audience is and to position yourself as a remedy for any potential pain points.
You want them to continually consume your content over time and throughout the buyer’s journey. This can be accomplished in various ways, including writing blogs and how-to guides, email campaigns, social media, SEO, etc. This generates interest and leads to further interaction with your target market, which is where lead generation comes in.
Lead Generation
Now that you have people interested in what you offer due to your demand generation strategy, it’s time to convert them into leads. Lead generation is a strategy to persuade people to take an actionable step, usually involving them in providing their contact information. In contrast, demand generation focuses more on establishing trust and increasing awareness.
This is where marketing and sales teams collaborate, with marketing teams capturing leads for sales teams to follow up on. Your B2B data can be used to create the ideal lead generation campaign with a compelling call to action.
There are many ways to generate leads, including cold calling, landing pages, gated content, and email marketing. High-quality data will ensure your lead generation strategy is personalized, targeting the right people and increasing the likelihood that prospects will become leads.
Lead Routing
Lead routing is a process that guarantees leads are routed to the appropriate salespeople when you have a flow of leads coming in. This process helps to ensure that potential opportunities are noticed and followed up on effectively.
They can be divided into various categories to maximize the likelihood that these leads will result in sales. Your B2B data will determine how you route your leads because it will be based on the lead’s origin, purchase readiness, location, etc.
These various data points will indicate what the sales representative’s next moves should be. Using a lead scoring process, you can quantify these data points and determine whether your potential customers need more nurturing or are ready to purchase.
Lead Scoring
In addition to the categories of leads discussed above, lead scoring is a methodology that sales and marketing teams can use to determine the sales readiness of each lead. Lead scoring entails determining which B2B data points constitute a sales-ready lead and then giving values to each data point to provide you with a final lead score.
Since your company may receive many leads, it’s critical to seize every chance that comes your way. You can increase the likelihood of turning leads into sales by prioritizing the hot leads and having teams concentrate more on them with the aid of lead scoring.
Finding your ideal customer will help you determine which data points to concentrate on because every business is unique. Discovering the steps your current customers took before making a purchase or the critical factors influencing their choice to do business with you will help you identify commonalities among them.
The observations made by your sales teams, such as preferred communication channels or specific value propositions made, can also be used to identify your ideal customers.
Usually, it will be a combination of the various data types discussed earlier. Still, it would help to use your data analytics to comprehend which data points are crucial for your company.
Data Analytics
B2B data analytics can be a game-changer when evaluating and improving sales and marketing strategies. Each step along the customer’s journey, from visiting your website to speaking with a sales representative, must be carefully examined to determine what is and is not working.
For instance, website analytics can offer a wealth of information about the origin of your traffic, the data collected from website visitors, and the tracking of website traffic and activities. Additionally, marketing campaigns must be closely watched to determine their efficacy by tracking open, reply, click-through rates, and many other metrics.
Analyzing trends or patterns in your data using all these metrics can help you, and then be used to optimize your sales and marketing strategies to improve campaign performance and overall conversions.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
You can now see which leads rank highest after you have completed the lead-scoring process. You could use this information to implement account-based marketing, supporting it with your data analytics.
What is Account-based marketing? As part of the ABM strategy, sales and marketing teams concentrate on one or a small number of high-value accounts. You can strategically and personally target each key stakeholder by determining which accounts offer the best chance of closing a sale.
Together, sales and marketing teams can develop an ABM strategy that will align their objectives and significantly improve the likelihood of success. Delivering high-value proposals suited for each decision-maker can be accomplished by creating targeted campaigns across appropriate channels. The number of interactions with prospects can be increased, the sales cycle can be shortened, and the likelihood of closing deals can all be improved with this coordinated effort.
How to get the most out of your B2B data?
Reach out to the contact or account to find out how likely they are to purchase from you, regardless of whether they had previously interacted with you (warm lead, such as when they downloaded an eBook from you) or not (cold lead). This is your first point of contact (and hopefully one of many).
A touch point is a way to reach out to a potential customer. You can do this through various channels, but typically you’ll use one or a combination of calling, emailing, and social media selling (e.g., LinkedIn). This is where the quality of your data becomes crucial.
A Guide to Data Quality Management
Low-quality data can include fewer data points, outdated information, or misspelled names; any of these things can instantly rule you out as a potential business partner. Additionally, lacking certain contact information in your B2B data can restrict your outreach options and harm your engagement rate, impacting the sales pipeline.
The quality of your data is essential if the price of your product or service is high. Higher pricing deals tend to result in longer sales cycles and involve multiple decision-makers. Understanding as much as possible about the contacts and accounts will better prepare your angle when presenting your solution.
Your first impression can make or break any potential deals from forming, so ensuring you are armed with accurate and up-to-date information will increase your chances of having a positive interaction. Demonstrating you know who they are and that you understand their potential pain points will be influenced by the quality of the data you have on them.
Once a rapport has been built, you will have more information about the potential customer, which you can use to guide future interactions and move them farther down the sales funnel. As you work to turn your leads into sales, this will probably be managed in a B2B CRM to help track engagement with your prospects. A B2B CRM can serve as a security measure and make your data accessible on the cloud, helping to ensure its security.
Where to store B2B data securely?
Regardless of where you obtain your B2B data, you must have a single, accessible location to store it safely. Having it stored on spreadsheets or anything similar will almost certainly give you headaches, but your sensitive information is also vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
Using a B2B CRM is the best way to store your data safely and in a GDPR-compliant manner. A B2B CRM (more specifically cloud-based) will ensure the most recent data quality measures are in place, in addition to tracking your deals and ensuring you are following up effectively.
Furthermore, along with the many other features available, you can be confident that your data will be recovered and used, increasing your sales over time.
How to maintain high B2B data quality?
B2B data can change quickly, so if you’re counting on a lot of information to get a comprehensive picture of a prospect, be aware that contacts may change jobs, employers, email addresses, and even their names.
Having a dedicated individual or team with a process for ensuring you have all the data points you need and confirming that it’s all accurate is a good idea. Use CRM or marketing automation tools to connect with customers and prospects. This will ensure you are confident in conveying the appropriate message and proposal to the appropriate person.
The following are some methods for maintaining high-quality B2B data
B2B data validation
Verifying the accuracy of your data is part of the validation process. Tools, services or your data provider may carry out this process (if you purchased from one). If this process isn’t finished, you risk calling incorrect numbers and experiencing high email bounce rates.
B2B data can be obtained from within an organization, from outside sources, or by paying a fee. B2B data is never static and constantly changing, so you want to ensure the data you receive is as fresh (as recently generated) as possible.
The data’s source will indicate whether it came from an existing source (such as a database or contacts list) or was created on demand (such as when a prospect left their contact information on your website or was obtained from an external source).
Cleansing your B2B data
Data cleansing, which typically entails deduplicating records or completely deleting them, is a process that ensures good data hygiene so that the quality of your B2B data remains high.
Incorrect data or irrelevant contacts will skew the analysis of any marketing campaigns you run and can harm your brand’s reputation by appearing spam
Data should be used immediately after being acquired to prevent decay. After some time, you should have a sizable list of contacts susceptible to having their data out of date. By cleaning your data, you can have a more accurate picture of your database and better tailor any marketing materials you produce to the requirements of your contacts and clients.
B2B data enrichment
Enriching your data means filling any gaps in your B2B database. This could be any piece of information, like a phone number, email address, or business name.
Some details may be distorted or missing altogether, depending on the data’s source. Data enrichment process can replace incorrect or missing data points with the appropriate information, giving you a complete view of your data.
This process can be carried out in various ways, but if the data still requires enrichment after being sourced, you can always leverage our B2B data enrichment services.
Conclusion
Understanding and effectively utilizing B2B data can provide a significant competitive advantage. By leveraging reliable data, businesses can make informed decisions, drive targeted marketing campaigns, and ultimately achieve greater success in the B2B domain.
So, embrace the power of B2B data and unlock new possibilities for your business growth. If you are looking for a way to source high-quality data while freeing your team from manual tasks, you can write to us at marketing@datamaticsbpm.com to explore how we could be the solution you need when sourcing B2B data.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
James Libera