Enough has been said about the importance of high-quality data for businesses. However, enough has not been done to ensure high quality data for businesses. Though marketers are well aware of the benefits and impact of clean data, they often fail to maintain the quality. This leaves the organization with bad and unstructured data.
With the rise in digitalization of business processes, organizations need to handle huge volumes of data. Moreover, the data keeps accumulating on a daily basis. Lack of proper data management can mean that organizations have to pay a high cost for bad data. Before diving into the cost of bad data, let’s understand what is bad data.
What is Bad Data?
Bad data resembles incorrect, inaccurate, or irrelevant data. A variety of factors can lead to bad data – errors in data entry, incorrect data formatting, or data that is out of date. Bad data can have serious consequences on business outcomes. It can lead to inaccurate conclusions and prove to be a roadblock in informed decision making. It is important to carefully check and clean data to ensure that it is accurate and useful for business campaigns.
What Constitutes Bad Data?
B2B data may include information about companies, such as contact information, industry, size, location, and revenue. Bad B2B data can have a negative impact on B2B sales and marketing efforts, as it may lead to misdirected or ineffective outreach, or even harm the reputation of the company.
While bad data comes in many forms, we’ve narrowed them down into 7 categories below:
1. Duplicate Data
Data duplication is a common problem where leads, accounts, and contacts inadvertent move identical duplicates, partial duplicates caused by human errors are more troublesome. Duplicate data causes various issues, including skewed analysis, inefficient workflows, storage problems, data retrieval challenges, poor personalization, and repetitive customer communication.
For instance, in Account-Based Marketing (ABM), personalized interactions are crucial. If a prospect is listed three times and receives the same emails repeatedly, they may view your campaign as automated and impersonal, reducing conversion chances.
Tips to clean Duplicate Data:
In the current data-rich business environment, relying solely on manual data cleansing is insufficient. Manual processes often struggle with handling partial duplicates effectively. Instead, consider investing in an automation platform capable of detecting, cleaning, and managing duplicate data. Such a platform can also be customized to sort and integrate duplicate data according to your company’s unique criteria.
2. Unprotected Data
Changes in security regulations have transformed the marketing landscape, largely due to the exponential growth of data. In tandem with this, mounting privacy concerns have strained the relationship between consumers and businesses, prompting adjustments in both regulatory measures and privacy-conscious behaviors of individuals.
The GDPR and CCPA stand out as significant privacy and data security laws that are now in force. Non-compliance with these standards or inadequate data security can result in substantial financial penalties. For instance, if a user’s data was collected without their consent or agreement to your data sharing and privacy policy, serious consequences may follow.
Today, businesses are increasingly prioritizing consumers in their decision-making processes, with digital permissions, opt-ins, and privacy notifications becoming the new norm. Without robust CRM hygiene, achieving compliance with these regulations becomes an uphill battle. Moreover, there’s the substantial risk of damaging your brand reputation. Even industry giants like Amazon and WhatsApp have faced public backlash and hefty fines exceeding $800 million and $270 million, respectively, due to suspected GDPR non-compliance.
Tips to clean Unprotected Data:
To adhere to data privacy regulations, maintaining a clean database is crucial. Here are practical strategies for cleaning insecure data:
- Eliminate unnecessary and unsafe CRM entries.
- Merge duplicate records to ensure data accuracy.
- Simplify your data infrastructure.
- Automate the lead-to-account linking process.
- Host your CRM on secure, legally compliant cloud software.
3. Outdated Data
Is a five-year-old report still relevant for your company’s decision-making?
Data’s importance can change quickly. Relying on outdated data for analytics is like using the wrong GPS and driving off the course. Imagine this: A website visitor initially fills out a form to access your resources. Over time, they engage more with your business by subscribing to newsletters and responding to emails. However, your CRM doesn’t reflect this updated information.
This means you’re still providing content suited for new leads, missing the opportunity to nurture those who are already engaged. Outdated data can also result from job changes, mergers, or outdated software.
Tips to clean Outdated Data:
Before migrating or integrating systems, it’s crucial to remove obsolete data. Identifying your company’s pivotal moments is a vital initial step. Consider removing historical data from your system. Having said that, manual cleaning can take days or weeks, and this is where outsourcing data cleansing process comes into play. Outsourcing can provide a dedicated team of experts who specialize in data cleansing, ensuring thorough and accurate results while freeing up your internal resources for other critical tasks.
4. Incomplete Data
When a record lacks crucial information needed for initial data processing before sales and marketing actions can take place, it’s considered incomplete. These data gaps pose significant challenges for sales reps, with approximately 45% of them facing issues related to missing information.
Unfortunately, incomplete data problems are quite widespread, making it harder to fully utilize the information you’ve gathered. Consider a situation where you have a buyer’s phone number but not their email address. This limitation prevents you from sending them important email campaigns, leading to missed sales opportunities. Furthermore, accurately scoring leads and segmenting prospects becomes a complex task when dealing with incomplete details.
Tips to clean Incomplete Data:
Cleaning incomplete data is crucial for effective sales and marketing. Use validation rules, regular audits, and automation to complete records. Manual verification, data standardization, and incentives can further enhance data quality.
5. Inaccurate Data
Inaccurate data is a major contributor to data pollution and can lead to various problems. Sales reps may input data correctly, but if it’s incorrect, it can cause significant issues.
It’s worth noting that a staggering 77% of businesses admit that inaccurate data affects their adaptability to change. Additionally, 41% of sales reps face challenges due to inaccurate data. This not only results in inaccurate reporting and poor decision-making but can also hinder opportunities to progress.
Tips to clean Inaccurate Data:
Accurate data is essential for effective marketing and sales campaigns right from the beginning. Hence, it’s crucial to track and prevent the entry of inaccurate data into the system. Use validation rules, regular audits, and data cleansing tools to prevent and correct inaccuracies. Invest in validation software, establish a feedback loop, and implement strong data governance for ongoing accuracy.
6. Inconsistent Data
While duplicate and inconsistent data may seem similar, they are distinct concepts. Duplicate data occurs when information is copied identically, while inconsistent data is non-standardized and does not conform to predefined rules.
Inconsistent data arises when multiple versions of the same elements exist in the system. For example, variations like CMO, Chief of Marketing, Chief Marketing Officer, and Chief Mktg Officer all refer to the same data field but are entered in different formats.
The presence of inconsistent data can significantly impact analytics and decision-making, as sales representatives must contend with various variables for the same lead information.
Tips to clean Inconsistent Data:
The most efficient method for cleansing this unorganized data is to adopt a centralized approach. Establish a uniform file-naming convention that your representatives strictly adhere to.
7. Hoarded Data
Many companies collect an ever-increasing volume of data with the aim of gaining valuable insights in the future. However, this data hoarding parallels real-life hoarding and comes with its own set of challenges.
Hoarding excessive data can slow down data exchange, inflate storage costs, and create data hygiene problems, making it difficult to extract essential insights for decision-making.
Moreover, different departments may have unique data requirements, further increasing data storage needs and negatively impacting coordination as departments struggle to access crucial data from one another’s storage.
Tips to clean Hoarded Data:
To steer clear of data hoarding, businesses can prioritize essential data and consolidate it in a central location. This streamlines the process of accessing analyses, ultimately enhancing team collaboration and efficiency.
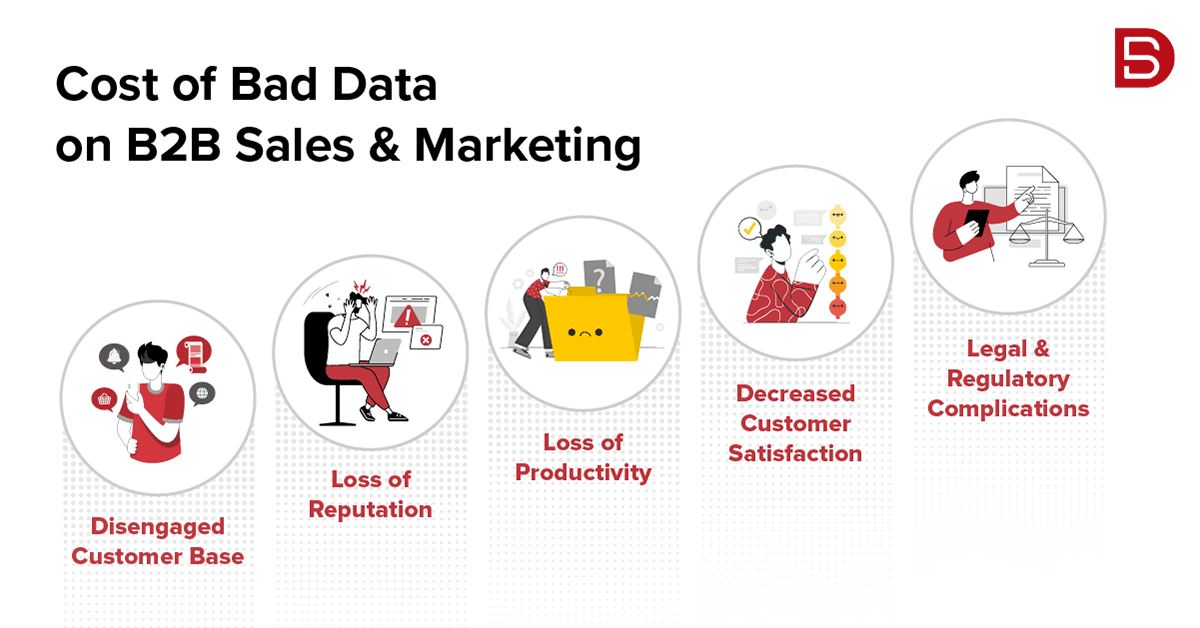
What is the Cost of Bad Data?
To quantify the exact loss that businesses face each year due to bad data would be outlandish numbers. According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), the amount of data in the world will rise from 33 ZB in 2019 to 175 ZB by 2025. That is an astronomically high number. As much as 30% of that data will need real-time processing and cleansing to make it suitable for any business use. Though there is no exact formula to calculate the cost of bad data, we, however, can highlight some of the most affected business areas due to bad data and you do the math.
• Disengaged Customer Base
93% of modern consumers receive marketing communication that has absolutely no relevance to them. This can lead to unsubscribes or backlisting of the entire domain and consequently lowering your sales. It’s always recommended to use a clean and updated B2B database to deliver personalized and relevant communication to your customer.
• Loss of Reputation
The internet remembers. Even before the GDPR, a minor slip-up caused due to bad data was enough to hurt the business reputation. It takes years of consistent efforts to build your brand and reputation. Bad data can hamper that in no time.
• Loss of Productivity
The cost of bad data isn’t limited to only your brand reputation and business conversions. It has a spiraling effect on your employee productivity too. Bad data can lead to wasted time and effort, as employees may spend time working with or trying to fix incorrect or irrelevant data. This can reduce productivity and efficiency, leading to lost time and resources.
• Decreased Customer Satisfaction
As mentioned before, bad data can lead to misdirected or ineffective outreach campaigns, which can result in frustrated or unhappy customers. This severely impacts customers’ trust, and they believe you don’t understand their expectations and needs. This increases the probability of losing them to your competitors.
• Inaccurate or Flawed Decision-making
Bad data can lead to incorrect or flawed conclusions, which can result in poor business decisions. This can lead to lost opportunities, reduced efficiency, and potentially even financial losses. Most of the business decisions are data-driven and that puts data at the core of every strategy. And a weak core can never yield great results.
• Legal and Regulatory Issues
Bad data can also lead to compliance issues and potential legal problems, such as failing to meet regulatory requirements or data privacy laws. With GDPR and CCPA in place, businesses must be extra careful when it comes to handling customer data and contacting them.
Impact of Bad Data
According to a study by IBM, the cost of poor data quality for businesses in the US alone is estimated to be around $3.1 trillion per year. This includes the direct costs of correcting errors and the indirect costs of lost productivity and missed opportunities.
Another survey by Gartner states that bad data can cost an organization nearly $13 million per year. More notably, 60% of businesses are not entirely aware about how much bad data actually costs them as they don’t measure the business impact.
It is important to note that the impact of bad data can vary depending on the size, industry, customers, services, and other factors. The cost of bad data can be much higher for certain industries or types of organizations. The healthcare or financial sectors are more likely to face severe consequences of poor data quality as compared to the other industries.
Why you Must Invest in B2B Data?
Businesses must invest in data to avoid the consequences of poor data quality. The cost of bad data can be difficult to recover from. However, with technology at your disposal, bad data problems such as missing data, data duplication, inaccuracy and reliability can be easily addressed through data cleansing and enrichment services.
According to Sirius Decisions, it will cost businesses just $1 to avoid data duplication, which, if left unattended, could build up to a $100 expense. Additionally, the other reasons to invest in B2B data are –
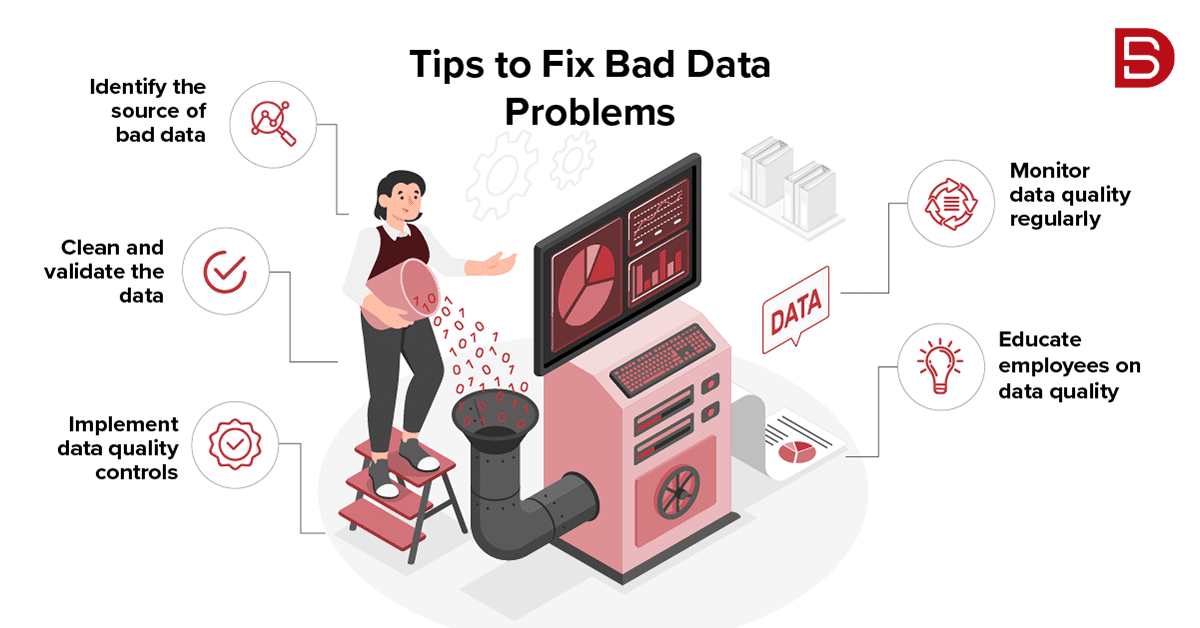
How to Fix Bad Data Problems
There are several steps businesses can take to manage and avoid the cost of bad data:
• Identify the Source of the Bad Data:
It’s important to determine where the bad data is coming from in order to address the root cause of the problem.
• Clean and Validate the Data:
Once the source of bad data has been identified, it’s important to clean and validate the data to ensure that it is accurate and up to date. This can be done manually or using automated tools.
• Implement Data Quality Controls:
To prevent bad data, businesses can implement data quality measures such as data validation rules and data entry guidelines.
• Monitor Data Quality Regularly:
Regular monitoring of data quality can help businesses identify and address any issues as they arise.
• Educate Employees on Data Quality:
Ensuring that employees are aware of the importance of data quality and the role they play in maintaining it can help reduce the incidence of bad data.
Conclusion
To avoid the high costs of bad data, organizations must create a reliable data ecosystem. It will attract a lot of investment in terms of time, cost and resources. Organizations can simply partner with a reliable B2B data solution provider. They have a deep understanding of data management and analysis and can bring a level of expertise and experience that may not be readily available in-house.
Partnering with a data solution provider can help businesses access the expertise and resources they need to effectively manage and analyze data, enabling them to make more informed decisions and drive growth. Moreover, they can save the cost of bad data and nullify the business impact of bad data.

James Libera